
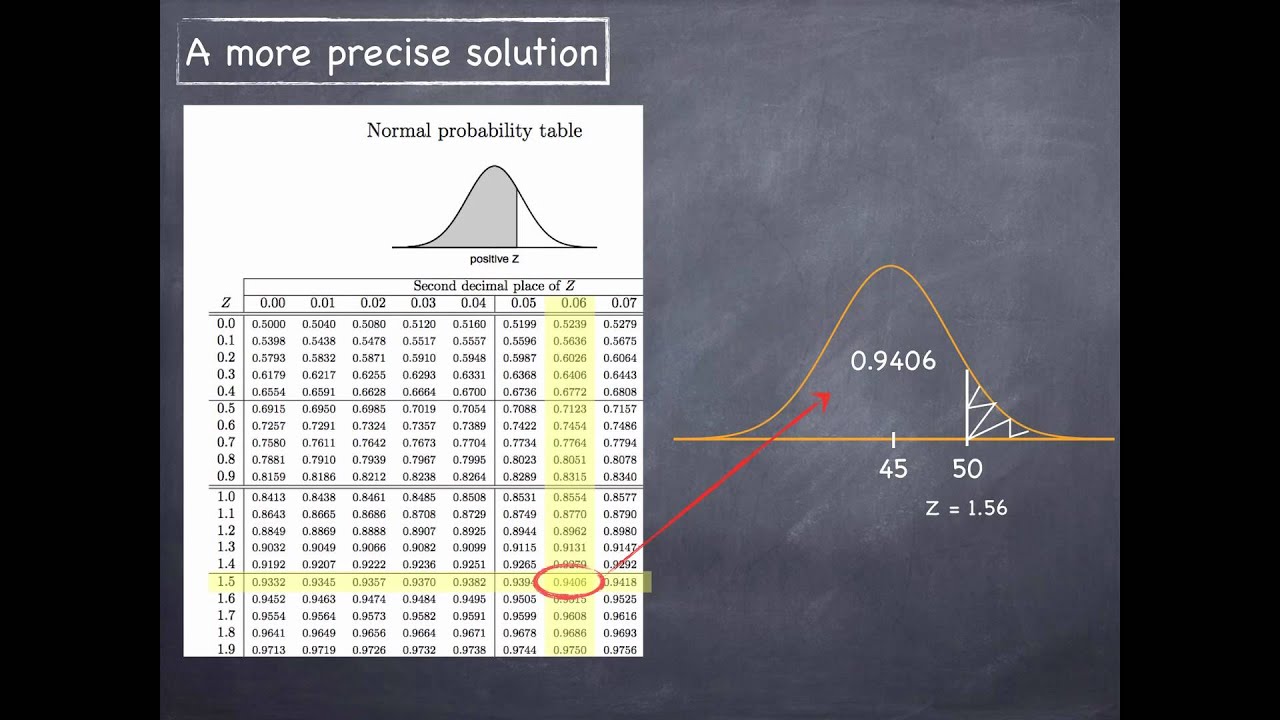
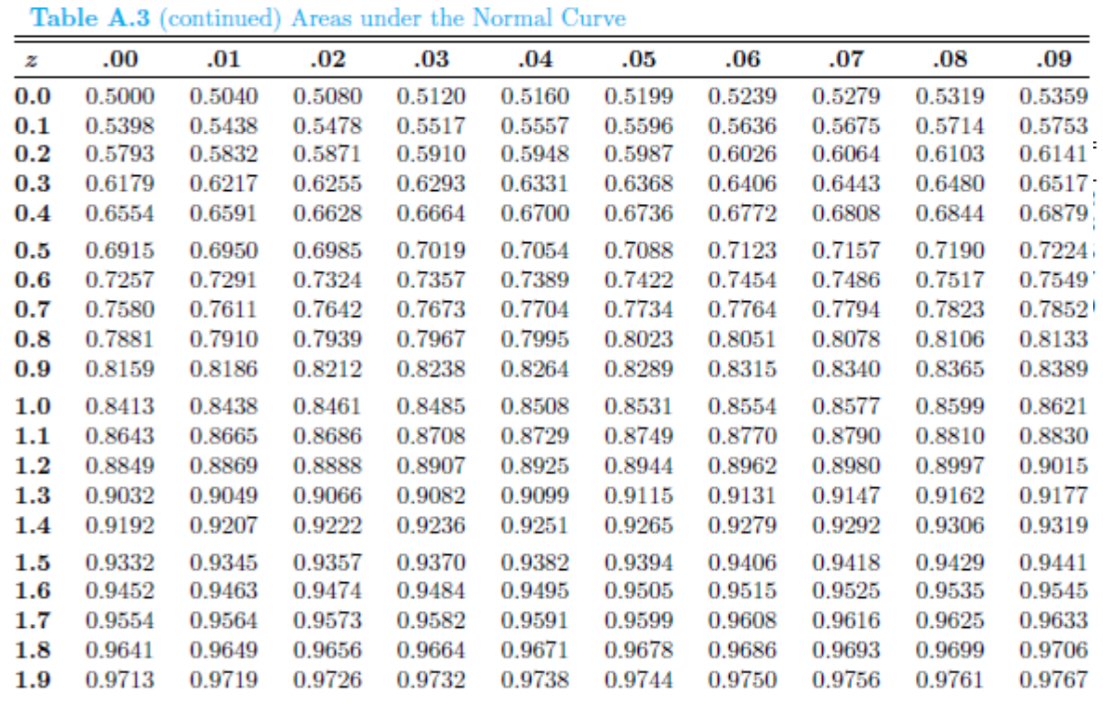
You can calculate the probability that your value is lower than any arbitrary X (denoted as P(x < X)) as the area under the graph to the left of the z-score of X. That means that it corresponds to probability. The total area under the standard normal distribution curve is equal to 1. If you input the mean, μ, as 0 and standard deviation, σ, as 1, the z-score will be equal to X. You can check this tool by using the standard normal distribution calculator as well. Every value of variable x is converted into the corresponding z-score.Total area under the curve is equal to 1 and.A standard normal distribution has the following properties: This is when you subtract the population mean from the data score and divide this difference by the population's standard deviation. You can standardize any normal distribution, which is done by a process known as the standard score. However, it's easy to work out the latter by simply taking the square root of the variance. It may be the case that you know the variance but not the standard deviation of your distribution. The number of standard deviations from the mean is called the z-score.
Generally, 68% of values should be within 1 standard deviation from the mean, 95% within 2 standard deviations, and 99.7% within 3 standard deviations.
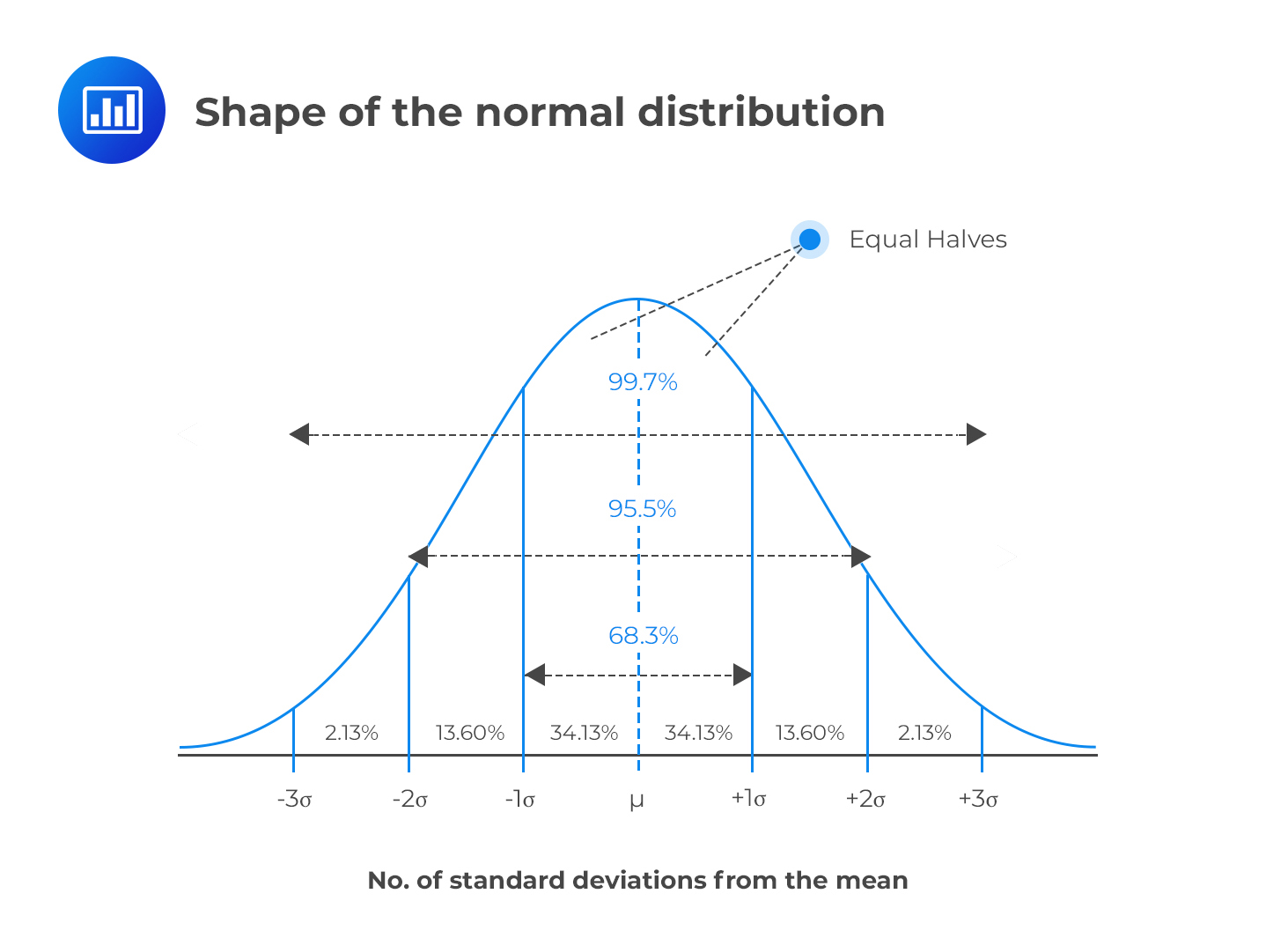
It describes how widespread the numbers are. As this distribution is symmetric about the center, 50% of values are lower than the mean, and 50% of values are higher than the mean.Īnother parameter characterizing the normal distribution is the standard deviation. In a normal distribution, the mean value is also the median (the "middle" number of a sorted list of data) and the mode (the value with the highest frequency of occurrence). Many observations in nature, such as the height of people or blood pressure, follow this distribution.

Most data is close to a central value, with no bias to left or right. The normal distribution (also known as the Gaussian) is a continuous probability distribution.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
